The System File Checker or sfc.exe is a utility in Microsoft Windows located in C:\Windows\System32 folder. This utility allows users to scan for and restore corrupt Windows system files. In this post, we will see how to run System File Checker and also see how to analyze SFC logs.
Run System File Checker on Windows
In Windows 11/10/8/7, the System File Checker is integrated with Windows Resource Protection, which protects registry keys and folders as well as critical system files. If any changes are detected to a protected system file, the modified file is restored from a cached copy located in the Windows folder itself.
So if at any point in time, you find that you have hacked some system files or maybe applied some tweaks or replaced system files, maybe while customizing your Windows, and you now find that your Windows is not working properly, you may want to consider running this utility first, before trying a System Restore. To do so, you will have to first open an elevated command prompt window.
To run the System File Checker in Windows 11/10/8/7, type cmd in the Start search box. In the result, which appears, right-click on cmd and select Run As Administrator.
You must be an Administrator running a Console Session
If you do not run the Command Prompt as Administrator, you will see a message:
You must be an administrator running a console session in order to use the sfc utility
Hence it is imperative that you do so.
Run sfc /scannow in Windows 11/10
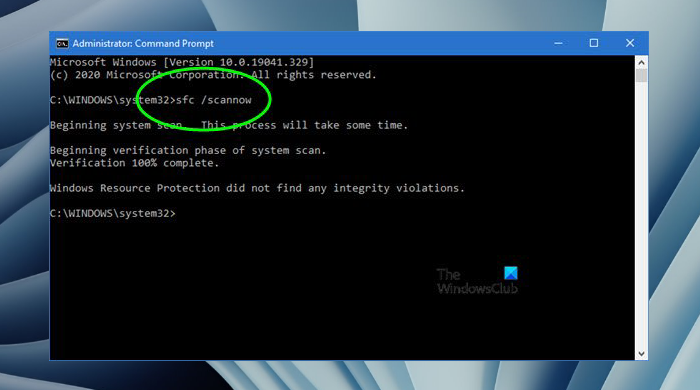
To run the Run System File Checker in Windows, open a command prompt window, type sfc /scannow, and hit Enter. The sfc.exe utility will run for a while, check the integrity of Windows system files, and if any corruptions are found, replace them on reboot.
Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested Service or Start the Repair Service
In case you are unable to start the System File Checker, and you instead get the “Windows Resource Protection Could Not Start the Repair Service” error, you may want to check up if your Windows Modules Installer service has been Disabled. To do so, type services.msc in start search and hit Enter. The status of this service should be set to Manual.
Alternatively, you can also download our very useful freeware utility FixWin and click on the System File Checker Utility button. This will run sfc.exe.
While running this tool, at the end of the scan, you may see any of these messages – some of which could indicate errors. They could be:
- Windows Resource Protection did not find any integrity violations
- Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files and successfully repaired them
- Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested operation
- System File Checker SFC cannot repair corrupted member file
- Windows Resource Protection found corrupt files but was unable to fix some of them
- Windows Resource Protection could not start the repair service.
If this happens, you may try to repair the Windows Component Store using DISM and see if it works.
See this post if SFC not working or will not run.
Read: DISM vs SFC first? What should I run first on Windows?
Run System File Checker Offline or in Safe Mode or Boot-Time
Simply boot into Safe Mode and follow the same procedure. System File Checker will run in Safe Mode too.
The /scanonce and /scanboot syntax have been discontinued after Windows XP and does not work on Windows 8 and later.
Follow this procedure if you want to run System File Checker in Safe Mode, Boot Time, or Offline.
You can also use the sfc.exe program to help you troubleshoot crashes that occur in the user-mode part of Windows 11 or Windows 10. These crashes may be related to missing or damaged operating system files. To do so, you may have to access the log files.
Read: How to scan & repair a single file using System File Checker.
How to view the SFC log file
The sfc.exe program writes the details of each verification operation and each repair operation to the CBS.log file. Each sfc.exe program entry in this file has a [SR] tag. The CBS.log file is located in the %windir%\Logs\CBS folder.
You can search for [SR] tags to help locate SFC.exe program entries. To perform this kind of search and to redirect the results to a text file, follow these steps:
Click Start, type cmd in the Start Search box, right-click cmd in the Programs list, and then click Run as administrator.
Type the following command and hit Enter:
findstr /c:"[SR]" %windir%\logs\cbs\cbs.log >sfcdetails.txt
The sfcdetails.txt file includes the entries that are logged every time that the SFC.exe program runs on the computer.
How to interpret the SFC log file entries:
The sfc.exe program verifies files in groups of 100. Therefore, there will be many groups of SFC.exe program entries. Each entry has the following format: date time entry_type details. For more details on how to interpret, visit KB928228.
Should I run ChkDsk or SFC first?
ChkDsk and SFC perform different functions—the first checks for disk errors while the latter for corrupted system files. We recommend running CHKDSK first, followed by SFC, and then DISM – and then SFC again if need be.
I hope this post helped you.